One of the most effective methods to manage and continuously improve information security and privacy aspects is the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle. In this blog, we dive deeper into the PDCA cycle and how it can be applied to information security and privacy.
Table of contents
What is the PDCA cycle?
The PDCA cycle , also known as the Deming cycle, is an iterative process for continuous improvement of processes and products. This cycle consists of four phases: PLAN plan, DO execute, CHECK check and ACT adjust. Each stage plays a crucial role in achieving a higher level of efficiency and effectiveness within an organization. By going through this cycle repeatedly, organizations can continuously improve their processes and results.
See 4-step plan below:
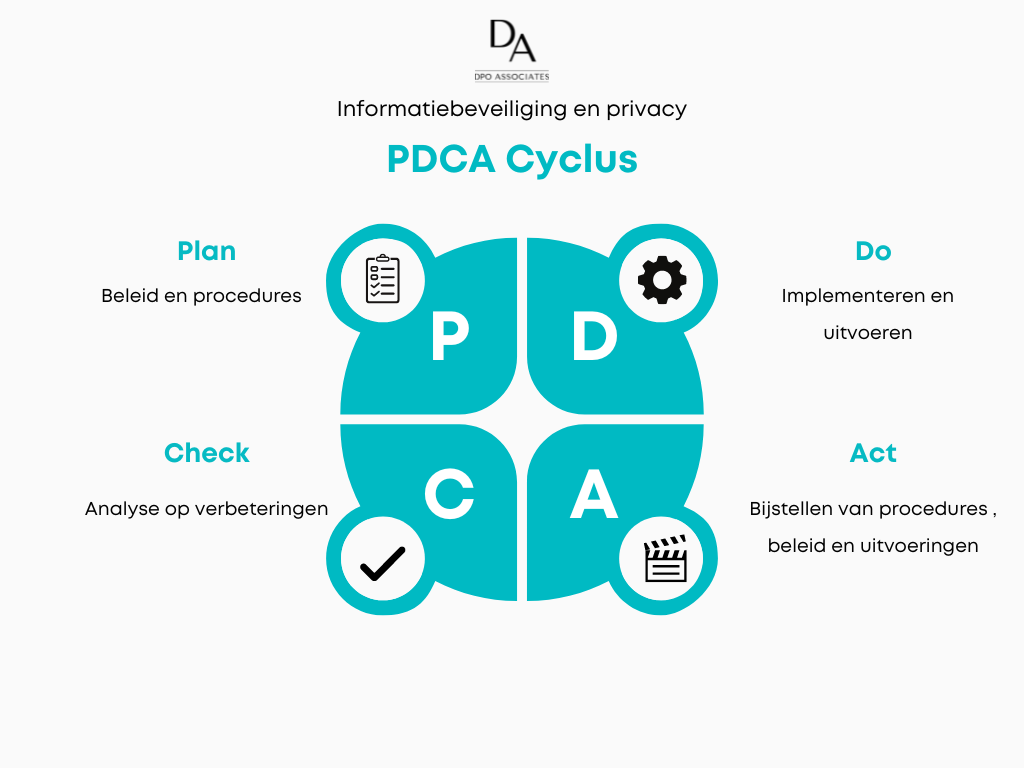
1. Plan: Preparation and Planning (Policies & Procedures).
This phase is all about creating an information security and privacy strategy. This includes:
- Risk Analysis: Identify and evaluate potential information security and privacy risks within the organization.
- Objectives: Set clear and measurable goals for protecting information and privacy.
- Policies and Procedures: Develop policies and procedures that provide the basis for security and privacy measures.
- Training and Awareness: Schedule training and awareness campaigns to educate employees about their role in information security and privacy protection.
2. Do: Implementation (Implement & execute).
During the implementation phase, the plans and strategies are put into practice. This includes:
- Implement Security Measures: Implement technical and organizational measures such as IS027001, firewalls, encryption, access controls and incident response protocols.
- Training Giving: Conduct scheduled training and awareness sessions for all employees.
- Communication: Provide clear communication channels for reporting security incidents and privacy issues.
3. Check: Evaluation and Monitoring (Analysis for improvements).
This phase revolves around measuring the effectiveness of implemented measures and identifying areas for improvement:
- Monitoring: Conduct continuous monitoring of security systems and privacy measures.
- Audits and Reviews: Conduct internal and external audits to assess compliance with policies and procedures.
- Incident Analysis: Analyze security incidents and privacy breaches to understand causes and consequences.
4. Act: Improvement (Adjust procedures, policies and implementations).
In the final phase, improvement actions are implemented based on the findings from the check phase:
- Corrective Actions: Implement corrective actions to address identified problems and weaknesses.
- Preventive Actions: Take proactive measures to reduce future risks.
- Update Policies: Update policies and procedures based on lessons learned and emerging threats.
Benefits of the PDCA cycle
Using the PDCA cycle for information security and privacy offers several advantages:
- Continuous Improvement: The iterative nature of the cycle ensures continuous improvement of security and privacy measures.
- Flexibility: The cycle can be easily adapted to changes in the organization or threat landscape.
- Engagement: It structures the involvement of all levels within the organization in improving information security and privacy.
Conclusion
The PDCA cycle is a powerful tool for managing and improving information security and privacy within organizations. By applying the cycle systematically, organizations can not only meet legal requirements and industry standards, but also strengthen the trust of their customers and partners. By continuously planning, executing, monitoring and improving, organizations stay prepared for the dynamic challenges of the digital world.









